Why it matters?
In dermatology, managing skin pigmentation is a complex task. It involves a detailed approach since pigmentation is affected by various factors, and addressing it requires a multi-pathway strategy. This is something often overlooked in mainstream marketing. However, the increasing interest in skincare solutions for pigmentation has led to a growing demand for effective treatments. Look at brands like Topicals! Addressing pigmentation requires a nuanced approach, divided into preparatory and intervention phases, each critical for achieving effective results.Yes The Priming Hype Is Important
Sometimes it may seem like an annoyance to not get the fun peel or extensive laser treatment without "priming." (using brightening and resurfacing skincare prior to a procedure) It may even seem like someone is just trying to upsell you, because YoU'Ve HaD ThE ProCEdUrE BeFoRe AnD ThEy DiDn'T SaY I NeEdEd ALL ThAt LaSt TiMe. Im sure! Although some procedures can be done without priming, tackling pigmentation effectively begins with preparatory steps aimed at priming the skin. This involves cleansing the epidermis of excess melanin and subpar dead skin cells to ensure the skin is in the best condition for treatment. Properly preparing the skin can enhance the effectiveness of subsequent treatments by up to 40%, especially in cases of superficial pigmentation.
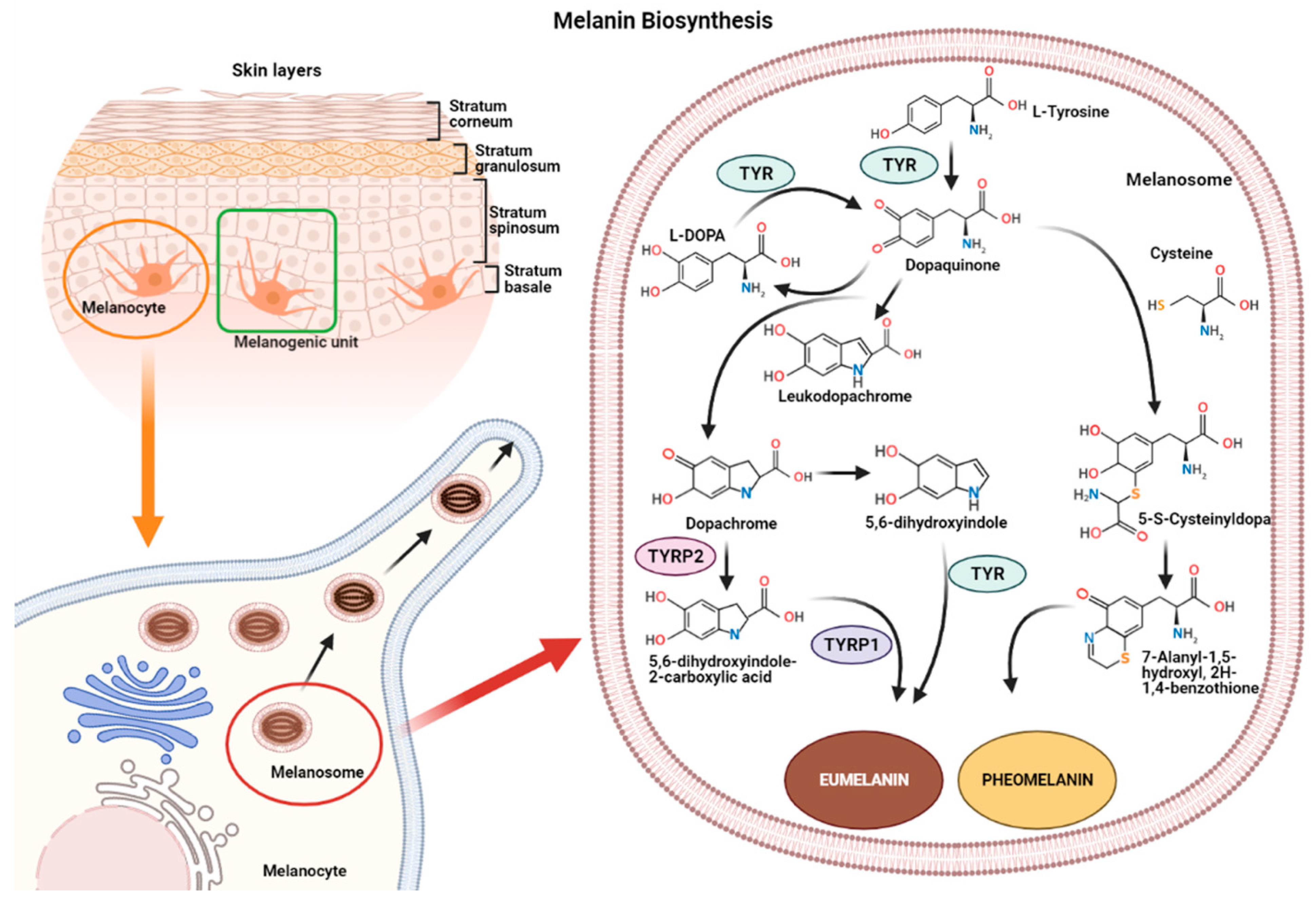
After laying the groundwork with preparatory measures, we pivot our focus towards directly targeting the melanogenesis process itself, aiming to address and lighten pigmentation more effectively. Given the complexity of melanogenesis, which involves multiple key pathways, a singular approach often falls short of achieving substantial results. While traditional treatments/products have predominantly centered on inhibiting the tyrosinase enzyme, recent advancements have expanded our toolkit, offering a wider array of strategies to combat pigmentation.
Understanding the Science Behind Melanogenesis
This process is influenced by a variety of factors, from genetic predispositions to external injuries, with ultraviolet (UV) exposure playing a significant role. Triggered by UV radiation, melanogenesis unfolds through a sequence of steps beginning with the production of proopiomelanocortin (POMC), followed by the activation of melanocytes by melanin-stimulating hormone (MSH), and culminating in the formation of melanin within melanosomes. This pigment, responsible for our skin color, is eventually brought to the skin’s surface, not only altering the complexion but also serving a critical role in protecting the skin from external threats.
Delving deeper into the mechanisms of melanin formation reveals opportunities for innovative treatments and products designed to manage pigmentation. Yet, the effectiveness of these solutions can be tempered by various factors, including the extent of cellular damage, such as the mitochondrial DNA damage found in conditions like solar lentigines. This type of damage often necessitates prolonged recovery periods, and the need for patience and tailored treatment strategies for different pigmentation issues.
The complexity of diagnosing and treating pigmentation extends further when considering conditions that might present as temporary discoloration or those deeply rooted, requiring more intensive interventions, such as laser therapy. This complexity accentuates the critical need for a thorough understanding of the potential underlying health problems—like tinea versicolor or acanthosis nigricans—that could manifest as changes in skin pigmentation. Recognizing these nuances is pivotal in addressing skin pigmentation effectively, and the interconnectedness between skin health and overall well-being.

acanthosis nigricans
___



II really enjoyed this section abot pigmentation. It really allowed me to have more explanation about it. Thank you for this in-depth explanation.